Costco Versus Walmart Versus Amazon?
Insight — China is becoming the proving ground for three very different retail futures. Costco is betting on controlled physical expansion plus digital pull, using a small but premium warehouse footprint to anchor membership loyalty while evolving toward app-driven engagement and localized supply chains. It’s disciplined, brand-centric growth aimed at long-term density rather than speed.
Walmart, through Sam’s Club, is defending its home turf with scale and execution. Its advantage is operational: dense store coverage, sub-one-hour delivery, and heavy logistics investment. Walmart is treating China as a digitally native retail market where fulfillment speed and assortment breadth matter more than experiential retail.
Amazon has opted out of the warehouse war entirely. Instead, it is monetizing China as a global supply engine—selling logistics, AI tools, and export infrastructure rather than groceries.
The result is not one winner, but three parallel strategies—physical loyalty (Costco), omnichannel dominance (Walmart), and platform monetization (Amazon)—each aligned to China’s accelerating, mobile-first consumer economy.
Costco
Expansion of Physical Warehouses (2025–2026)
- Pipeline for 2026: Globally, Costco plans to open 35 new warehouses (30 net new) in fiscal 2026, which begins September 1, 2025. A “significant number” of these are slated for international markets, specifically targeting high-potential areas like China.
- Growth Potential: Analysts note that based on U.S. per capita metrics, China theoretically supports hundreds of warehouses, though Costco is maintaining a “slow and steady” approach to ensure operational discipline.
Digital and Online Store Evolution
- “Digital-Only” Memberships: Management has hinted at potential digital-only membership tiers to capture younger, tech-savvy demographics in Asia who prefer shopping via mobile apps rather than visiting physical stores.
- App Improvements: Throughout 2025, Costco has focused on upgrading its mobile app with features like personalized product recommendations, searchable purchase history, and a digital wallet. For 2026, the company plans even more personalized digital communication to deepen member engagement.
- Last-Mile Delivery: To compete with local rivals, Costco is increasingly utilizing partnerships for same-day delivery from its warehouses, extending the convenience of its online store without heavy capital investment in its own fleet.
Operational and Economic Strategy (2025–2026)
- Supply Chain Localization: To mitigate global trade tensions and tariffs introduced in 2025, Costco is localizing its supply chain within China, particularly for Kirkland Signature products, to better serve the regional market.
- Membership Revenue: The full impact of the September 2024 fee increase is expected to flow through the 2025 and 2026 financials, providing capital for further expansion in mainland China.
Walmart Defending “Home Turf”
Rapid Physical Expansion
- Expansion Pace: 2025 is Sam’s Club’s busiest expansion year ever in China, with 10 new stores opened.
- 2026 Pipeline: Walmart plans to open nearly 20 more stores during 2025–2026. A “mega store” in Tianjin—its largest by operational area in northern China—is specifically scheduled to open in 2026.
- Long-Term Goal: Walmart intends to maintain an average growth rate of 8 to 10 new Sam’s Club stores annually after 2025.
Digital and Omnichannel Dominance
- E-commerce Leadership: Digital sales now account for more than 50% of Walmart’s total China revenue.
- Delivery Speed: Walmart offers delivery in under one hour for roughly 80% of its digital orders in China.
- Fulfillment Strategy: Its 2026 Tianjin mega store will integrate a physical warehouse with 20 digital fulfillment centers to maximize regional delivery coverage.
Supply Chain and Market Strategy
- Tariff Response: In 2025, both Walmart and Costco pressured Chinese suppliers to absorb the cost of U.S. tariffs to keep prices low for members. Walmart has faced specific scrutiny and “implied threats” from Chinese officials for this aggressive price-cutting stance.
- Product Differentiation: Sam’s Club is focusing on unique, high-quality items that are difficult to find elsewhere to attract China’s growing middle- and upper-income urban families.
- Logistics Investment: Walmart recently announced a $1.2 billion investment to upgrade its logistics operations in China to support this rapid expansion.
What is at stake?
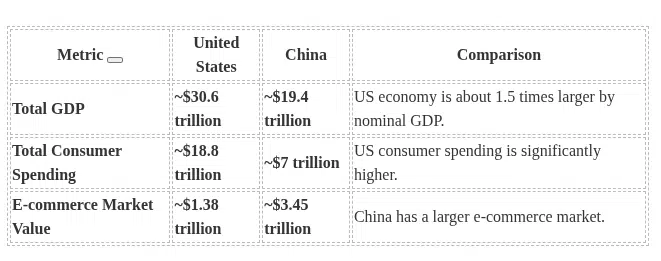
China US Market Size and Projections: 2025
Projections for 2026 and Beyond
- Growth Rates: China’s GDP is forecast to expand by approximately 5.0% in 2026, while the US is expected to see slower growth, with projections around 1.8% real GDP growth in 2026.
- Closing the Gap: Consumer spending in China is set to more than double by 2030, potentially reaching levels similar to current American consumer spending, driven by rising urban incomes and a deeply embedded digital ecosystem.
- E-commerce Dominance: China will continue to drive the global average for e-commerce penetration, which is expected to remain significantly higher than in the US, as mobile devices dominate the shopping experience in Asia.
- Government Role: China’s government continues to prioritize boosting consumption and stimulating domestic demand through various policy levers, though effectiveness is debated amid ongoing property market challenges and trade tensions. In the US, consumer spending accounts for roughly 70% of GDP, making it a primary driver of the economy, but it is susceptible to interest rate hikes and tariff impacts.
Amazon
Strategic Pivot: From Local Retail to Global Export
- Logistics as a Service: In late 2025, Amazon expanded its Multi-Channel Fulfillment (MCF) service to handle orders for its rivals, including Walmart and Shein. This allows Amazon to profit from its competitors’ sales by providing the backend logistics for independent sellers on those platforms.
- Shenzhen Global Smart Hub: In December 2025, Amazon announced the world’s first Global Smart Hub Warehouse (GWD) in Shenzhen, set to be fully operational by March 2026. This facility allows Chinese sellers to ship goods to one location for automated global distribution, directly countering the localized supply chains Costco and Walmart are building.
Competing on Price and Selection
- Amazon Haul: Launched in late 2024 and expanded throughout 2025, this in-app service targets the same “affordable luxury” and “bulk value” demographics as warehouse clubs by offering low-cost items shipped directly from manufacturers.
- Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Tools: For 2026, Amazon is rolling out agentic AI tools (like “Project Amelia” in Chinese) to help local manufacturers bypass traditional retailers and sell directly to international consumers, an area where physical warehouses like Costco have limited reach.
Supply Chain Realignment (2025–2026)
- Manufacturing Diversification: Amazon plans to shift a significant portion of its private-label manufacturing and AWS hardware production outside of China by 2026 to mitigate geopolitical risks.
- US-Based Stocking: To maintain delivery speeds that match Walmart’s “one-hour” delivery in China, Amazon is pressuring its Chinese vendors to maintain stock in U.S.-based warehouses rather than relying on direct-from-China shipping for its core markets.