IoT Market Research Predictions 2021
Great report from Kinsey listing markets for IoT. It’s hard to argue with RFID checkout and self-checkout payment is growing leaps and bounds. The old stand at cashier model is at or past the tipping point. They point to cost reductions in the store.
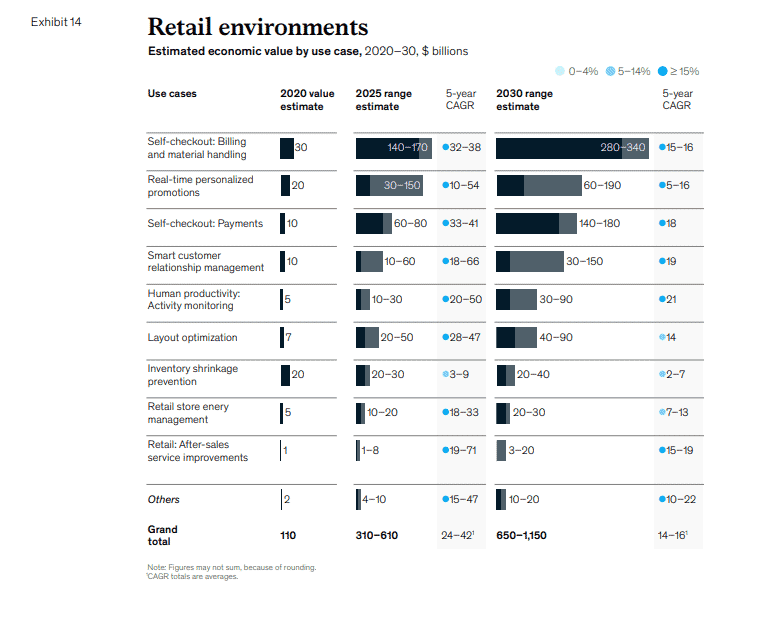
Key point for us — Adoption of self-checkout use cases is expected to increase from a relatively low 15 to 35 percent of organized retail today to 80 to 90 percent in 2030.
In Brief
- Markets include:
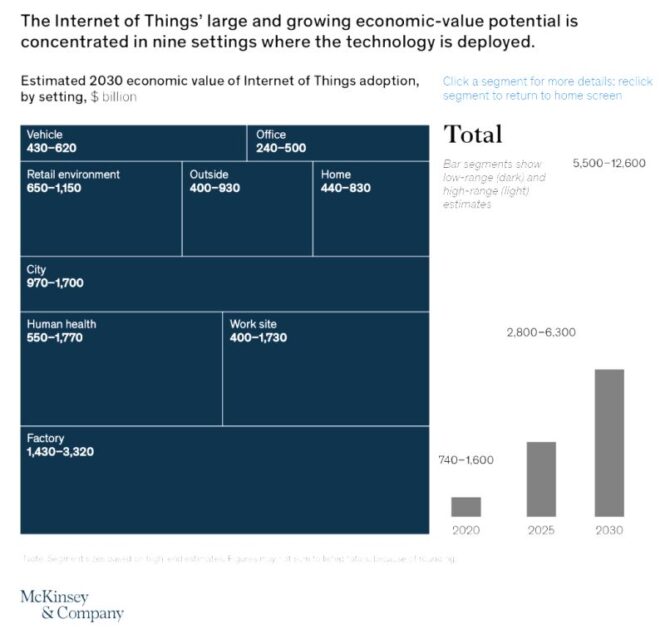
- Human Health (2)
- Home (7)
- Retail (5)
- Offices (8)
- Factories (1)
- Work Sites (3)
- Vehicles (8)
- Cities (4)
- Outside (9)
- Economic Value for all projected to be between 5.500 and 12,600 (billions)
- Top segments in Retail are Self-Checkout, Personalized Promotions and Payments
- 2015 actual numbers slightly exceeded lower range of predictions then
- Examples used Amazon, Sephora
- Interestingly Kinsey groups EV in the Outside segment
Excerpts
- The 2030 IoT value potential of the developed world will account for 55 percent of the global total, decreasing from 61 percent in 2020. China is becoming a global IoT force, not only as a manufacturing hub and technology supplier but also as an end market for value creation. By 2030, China could generate about 26 percent of the total global value from the IoT, equal to the potential of all emerging markets combined (and above its share of the global economy of about 20 percent).
- Retail — Potential for economic impact in 2030 Overall, we estimate that applications of the IoT in the Retail Environments setting have an economic value of $0.6 trillion to $1.1 trillion, representing 9 to 12 percent of potential economic value across all settings (Exhibit 14).
- Today, only a few companies are taking advantage of the wealth of data now available. 74 In a subset of stores, particularly in apparel, retailers are considering RFID-based self-checkout; this technology could become ubiquitous by 2030. In general, stores will adopt self-checkout so they can allocate in-store labor to solve other issues or do what robots cannot yet do (for example, packing boxes or bags for omnichannel orders) when these activities provide a higher return on investment. There is one important caveat: the COVID-19 crisis has had a profound impact on the retail sector, causing significant uncertainty on long-term adoption. On the one hand, the pandemic has accelerated the demand for self- serve and touchless checkout; on the other hand, retailers, particularly smaller ones, have been caught in the financial turmoil of the crisis and have limited cash to make such investments. Recent labor shortages and rising cost also increase pressure on retailers to adopt self- checkout use cases.