Reprinted from GGS October 2021
Global retail sales were projected to amount to around 26.7 trillion U.S. dollars by 2022, up from approximately 23.6 trillion U.S. dollars in 2018. With such growth and disturbances across supply chains that started in 2020, many companies are looking for ways to streamline their business processes, cut costs and improve efficiency. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) software can be a solution to many problems that retailers are facing. In this article, we will show the benefits of process automation in the retail industry.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA), and how to use it in the retail industry?
RPA, or Robotic Process Automation, is the name given to software that can perform tasks at the user interface (UI) level. Robots can do anything that employees do and free them from tedious, mundane, and time-consuming tasks. Because RPA is great for repetitive tasks that have to follow a specific set of rules, there are multiple areas of business where these robots thrive.
Retailers have to deal with multiple challenges, and the potential of automation can be a game-changer for them. A good example of a multinational company embracing Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can be Walmart, which uses over 500 bots not only to automate tasks such as answering employee questions or retrieving useful information from audit documents but also to track the inventory flow, to identify slow-moving items and deadstock.
Even a small process improvement can turn into huge savings when we consider that Walmart’s back-office processes 200 Million+ Account Receivables and 2.3 Million+ employee payrolls.
How to use RPA in the retail industry?
Implementing RPA in the retail industry improves the productivity and accuracy of multiple processes, which don’t have to be manually performed by humans any longer.
RPA use cases for retail are automatic pricing and inventory adjustment, as well as using bots to obtain data from customer complaints and opinions in real-time. Such data can be then used by multiple departments in the enterprise, including marketing, sales, research & development, and manufacturing.
But there is more to gain in retail with RPA, as a vast number of tasks can be automated in many areas, including:
- store planning,
- inventory management,
- product categorization,
- logistics and supply chain management,
- business and sales analytics,
- launching new products,
- customer support management,
- consumer behavior analysis,
- automated customer loyalty programs,
- EOD and Month-end Reporting,
- integrating brick-and-mortar stores and e-commerce platforms,
- other uses like managing human resources and accounting,
Fast market growth will force many enterprises to reorganize their business processes, especially those connected with e-commerce, to keep up with demand and remain competitive.
Benefits of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in retail
With a lack of programming integration, quick implementation potential and ability to work 24/7/365 RPA software can huge potential to support retailers in dealing with main challenges that the industry is facing, such as maintaining a high level of inventory, managing the workforce, and providing fast and quality customer service.
The main benefits of RPA use in the retail industry are:
- improving product availability,
- reducing errors in business operations,
- freeing up employees time to focus on customer experience,
- providing real-time analytics,
- speeding up the order and return processing,
- enhancing customer support,
- allowing easy application integration,
- easy collection and compilation of data for auditing,
- optimizing operational efficiency and costs,
Let’s dive deeper into the use cases of RPA in the retail industry and discover opportunities.
Store planning with robotic process automation
In a retail store, the speed and efficiency of how customers can move around are extremely important, as it directly affects the number of sales that are made. Customers that are able to find what they are looking for easily are more likely to spend more time and money in the store, compared to irritated customers that cannot find what they came for.
Retailers are optimizing store space to affect the travel time, accessibility, flexibility, and maneuverability of shoppers. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) software supports retailers in anticipating customer expectations better by segmenting store layouts according to consumer demographics and preferences.
Analyzing the customer behavior for picking the right store layout is challenging, as there are many variables that have to be taken into account. RPA can easily access existing databases and gives retailers access to more accurate information to compare on a store-by-store basis.
Such data should be gathered and compared constantly as customer behaviors are changing and store layout might have to change as well to streamline the shopping experience and boost sales.
The most common variables used for store planning, that can be collected and prepared to analyze are:
- visit duration,
- number of sections visited,
- number of stops during the path,
- location of hotspots and heatmaps.
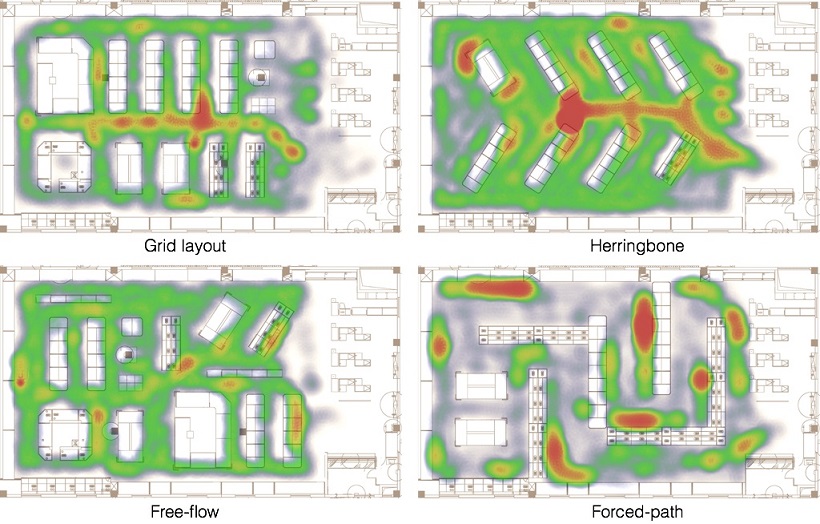
For example, RPA software can be used to track hotspots (places where the most activity within the store takes place) on different layouts and compare them in similar circumstances – here are examples of different store layouts:
Source: https://shoppermotion.com/
The main advantage that RPA software has over humans is that it can gather and compile data faster and support human analysts in organizing the store to fit customer expectations, improve user experience, and boost profits.
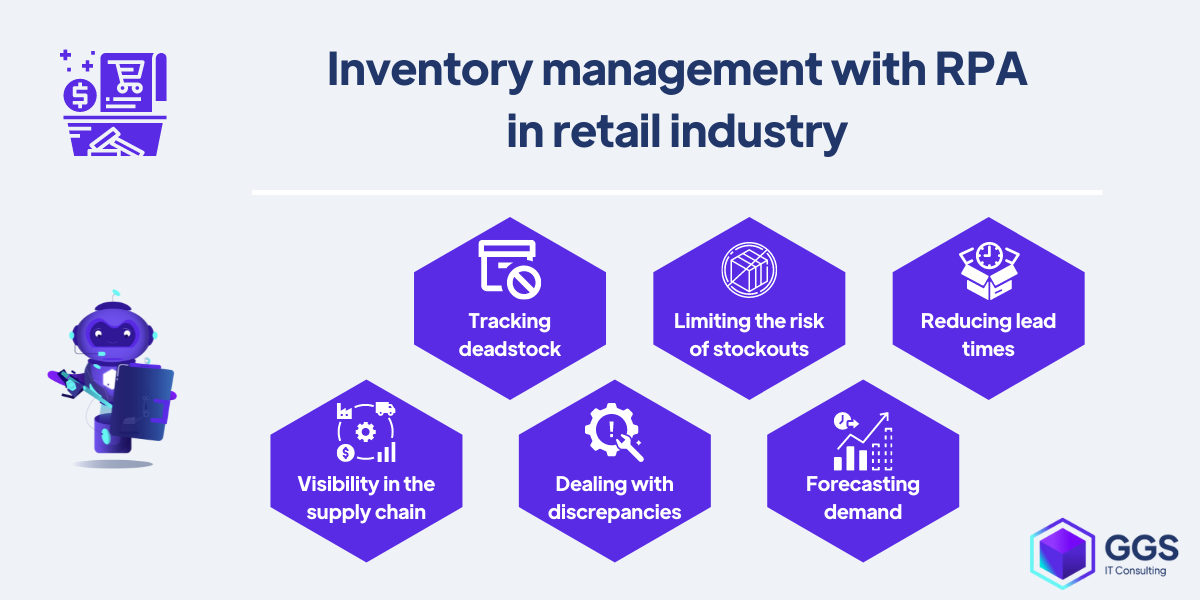
Retail inventory management with RPA
With proper process discovery, mapping, and thoughtful implementation of RPA software, it can be really valuable to any retail company. The uses of RPA robots are not limited only to monitoring inventory, generating notifications, or transferring data between systems. It can be also supported by AI and Machine Learning capabilities, to track patterns and help to avoid problems with an inventory shortage.
Examples of inventory management with RPA software include:
- tracking and dealing with deadstock,
- avoiding or limiting the risk of stockouts,
- reducing lead times,
- increasing visibility in the supply chain,
- dealing with inventory discrepancies,
- demand forecasting.
Especially the case of forecasting is important for companies as it helps to keep track of sales and demand so retailers can better manage purchase orders. A good example of this was presented by UiPath, and includes the following steps:
- data extraction from a CRM by a robot,
- use of a machine learning model to predict sales,
- human interaction to accept numbers forecasted by RPA,
- adding data into a purchasing platform and proceeding with the order by the bot.
In this video, we can see the entire process, that without the use of RPA would require employees to go through the stocks, extract, read and interpret reports and then make inventory decisions. This would require manual data input, manual reading, and manual work, and can be done easily with the use of UiPath software:
In the case of companies that combine retail with e-commerce platforms, it could be valuable to read more about how inventory management can be streamlined also in the case of online systems – you can learn more from our article “Effective e-commerce inventory management with RPA”.
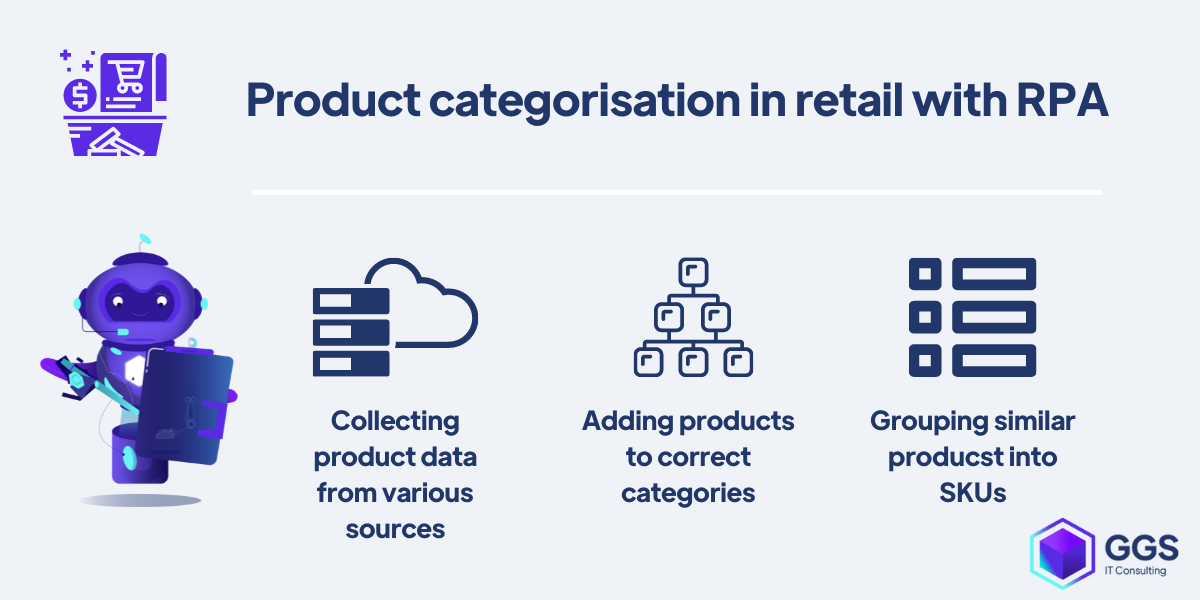
Automated product categorization in retail
Most leading retailers need to think about their product categorization from a warehousing point of view and having in mind e-commerce, as they are already selling products online or are planning to do so shortly. Having unified categorization helps not only with more accessible and faster orders but is critical for customer experience.
When a particular product is available on an e-commerce website, but the customer is unable to find it because of poor product categorization done by the retailer, it directly impacts sales and business effectiveness.
Having a product categorized not only by type but also various other features increases the chance of it being found by the customers, leading to more sales and business success.
RPA combined with AI capabilities can categorize items based on product mapping rules, customized at the implementation stage. Data about products can be captured from various sources, including uploaded pictures.
RPA will automatically detect multiple product features, giving much more options than only the general category to be assigned, for example:
- color,
- size,
- pattern,
- brand,
- technical specifications,
- and much more.
One of the best examples of this use of Robotic Process Automation was described by EverestGroup. It mentioned a case of a global company that faced challenges in product categorization involving harmonizing product information from global Stock Keeping Units (SKUs) to local SKUs. Implementation of cognitive automation helped to achieve 98,5% accuracy in product categorization.
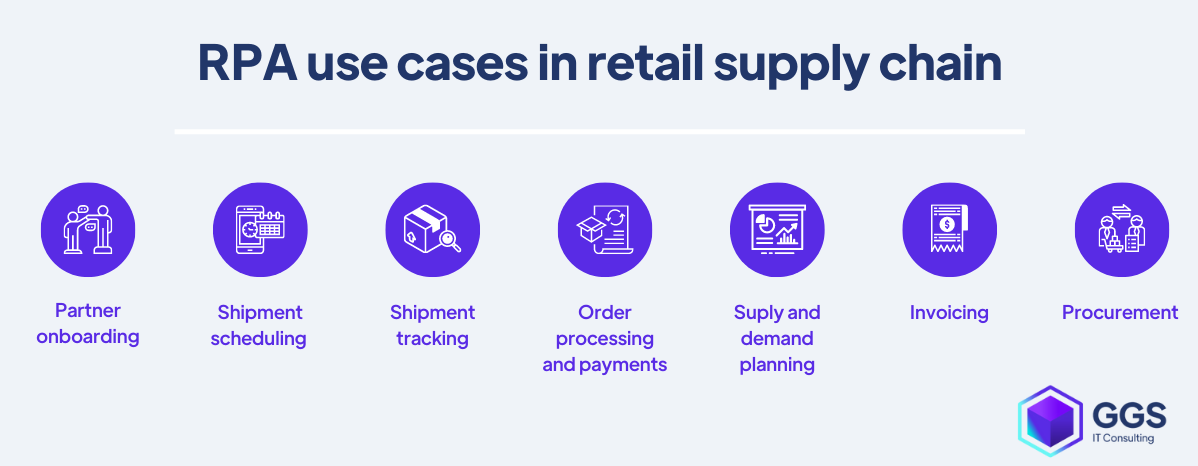
Logistics and supply chain management with RPA
Automation of multiple routine processes that can be identified within the supply chain can radically improve efficiency and bring down operation costs. Opportunities that Robotic Process Automation brings will be beneficial for retail companies worldwide.
Multiple processes can be automated within areas such as:
- supply and demand planning,
- purchase order management,
- invoice management,
- partners onboarding,
- shipment scheduling and tracking,
- procurement.
With vast amounts of data gathered, stored, and analyzed, each improvement achieved through the implementation of RPA in that field can bring fast ROI and strengthen the company’s market position.
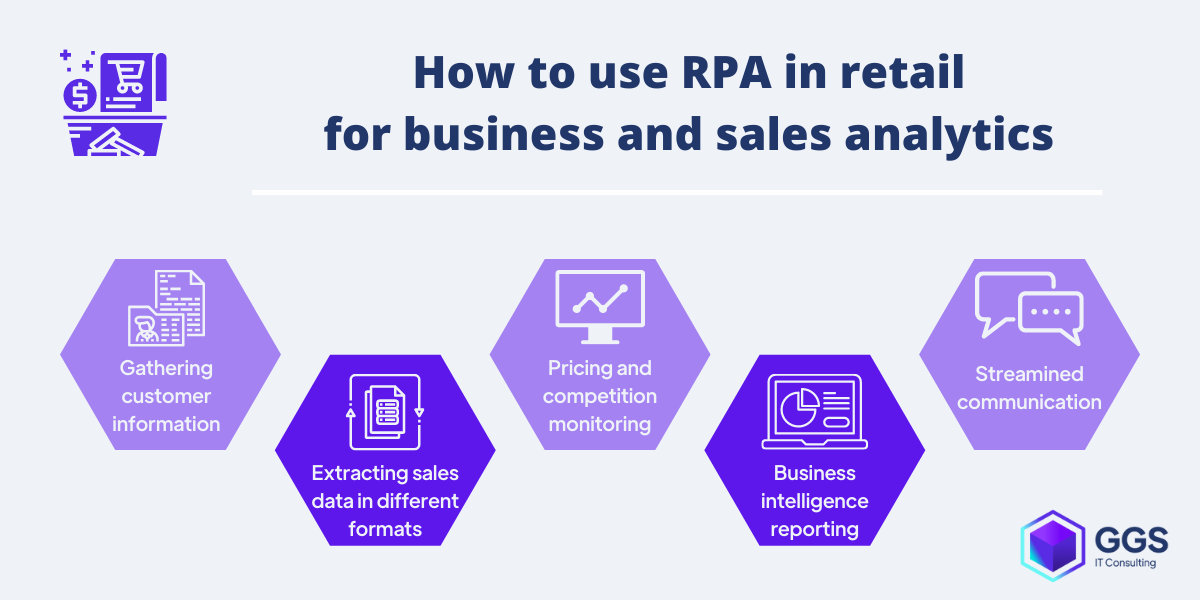
Business and sales analytics automated with RPA
In many cases, one of the barriers blocking the full potential of automation is a lack of imagination. With the growing use of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and natural language processing combined with RPA software new automation opportunities arise. In the case of sales analytics use of RPA might not always be obvious, as bots are not designed to be by any means an analytics tool.
But the real potential of RPA in service of sales analytics lies in its capability to collect data from various sources, without the need for programming integration, in different formats, and aggregating them in desired, easy to understand format.
With enormous amounts of data scattered across many departments and systems, not always integrated, the possibility to gather them and compile them to get a full picture of retail effectiveness cannot be ignored.
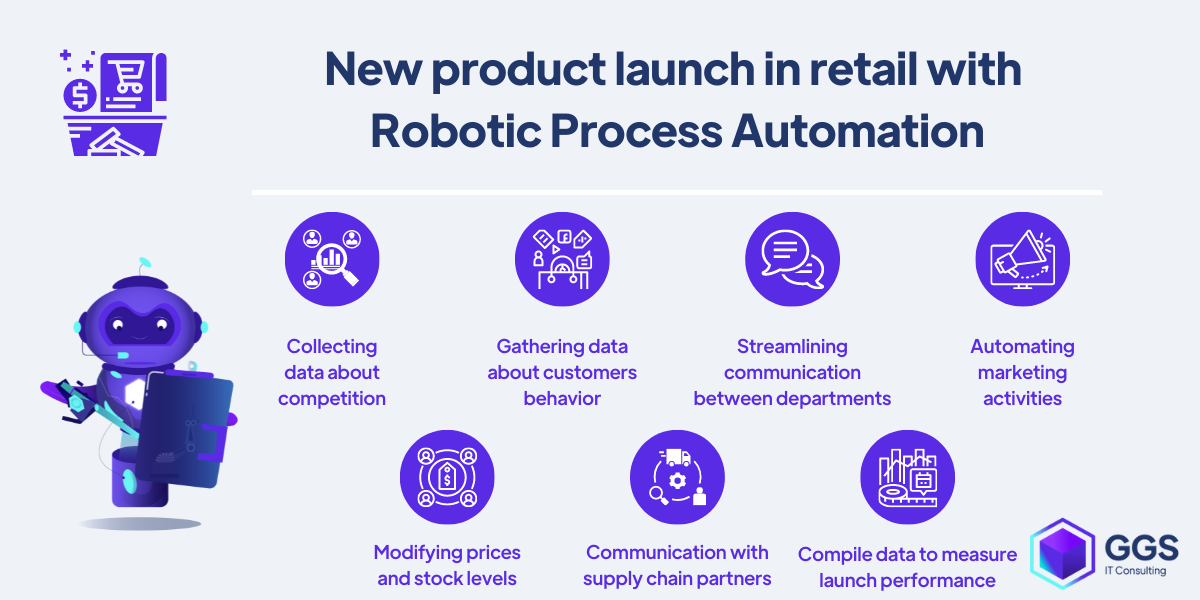
Launching new products in retail supported by RPA
A product launch in retail is a complicated process of planning, releasing, and tracking the performance of new offers on the market. To succeed, requires strong cooperation between multiple departments, including product development, marketing, sales, customer support, and HR.
Because RPA is not an out-of-the-box software type it can be used effectively on all stages of product development and launch, not only for a single, specific process. The only limitation is understanding the full potential of RPA and using it to optimize manual processes, such as:
- collecting and compiling data about the competitive landscape to analyze,
- helping to gather data about customers behavior,
- streamlining communication between R&D, manufacturing, and marketing departments,
- automating marketing activities,
- modifying prices and stock levels in response to customers reactions to the product,
- supporting communication with supply chain partners,
- compile data to measure launch process performance.
Such a complex process as a new product launch requires improved transparency and collaboration to be successful, and properly implemented RPA software can be a factor that will limit related risks.
Customer support management in retail with RPA
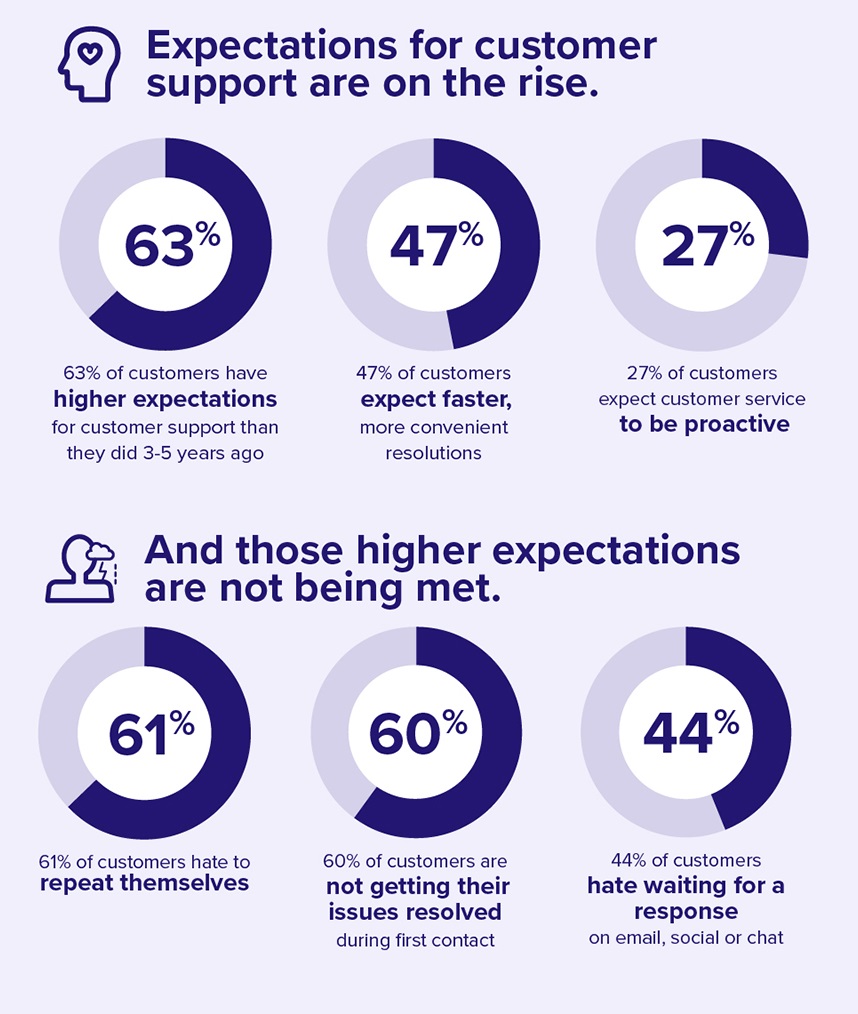
Retailers spend more and more resources to maintain high customer retention and customer satisfaction. Some of the activities might include streamlining checkout processes or monitoring customer complaints, but only with enough and correct data enterprise can plan actions that will make a difference. It is extremely important because customers’ expectations for high quality and fast support are rising.
Source: based on Netomi Pulse Report
RPA use cases for customer service in retail include:
- reduction of Average Handle Time in a call center,
- improving First Call Resolutions (FCR) rate,
- combining chatbots with RPA and AI,
- review tracking and management.
In the case of retailers that are selling their products not only in physical stores but also online, the level of complexity in customer support increases and they can make even bigger use of RPA solutions. We have described those potential gains in our article “Use cases of RPA improving e-commerce customer service”.
Consumer behavior analysis in retail
Retailers are constantly trying to improve the shopping experience, and with new technologies, they are able now to analyze the complete customer journey also in brick-and-mortar stores. We already mentioned customer behavior analysis in the context of store planning with the use of RPA, but there is more in it to gain than only that.
A good example of making full use of automation potential is Tesco, a multinational retailer of general merchandise. Tesco uses not only RPA software, but most of all combine it with AI and Machine Learning. Such a combination allows this retailer to track customer behavior patterns and respond in real-time, increasing sales and customer satisfaction.
An example of this strategy can be a case of supplier-retailer cooperation with Kellogg. Tesco gathered data from POS in certain supermarkets in real-time, feed them to AI, and used it to identify purchasing patterns. That information was used to adjust the shipping schedule of the supplier, resulting in recapturing more than $4million in lost sales for Tesco.
For such real-time data capture, RPA can be a perfect fit, especially when companies are using older systems, and integration with them could be expensive.
Another benefit of RPA software use is that it can help companies to make use of historic data about sales that otherwise could be wasted – not only data in digital form from legacy systems, but also paper documents, that can be read with the use of Optical Character Recognition, and used to better understand customer behavior and shopping patterns.
Capturing customer data from external sources
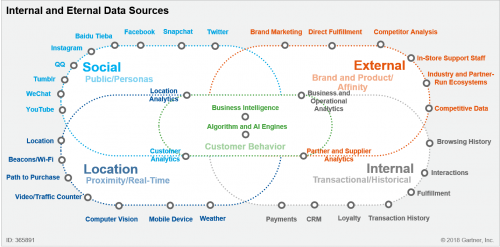
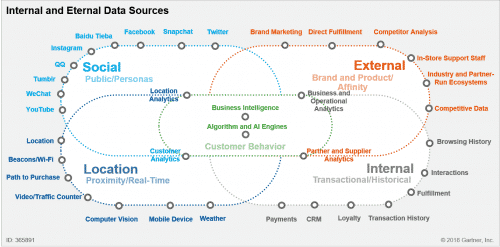
As pointed out by Gartner, customer data availability, quality and consistency are major issues when it comes to behavior analysis. When all internally available data are gathered, retailers often find that there are many gaps that prevent behavioral segmentation and require additional, external data.
An example of data sources from where customer information can be obtained was presented by Gartner in article about Advanced Behavioral Segmentation in Retail:
Source: Gartner
Automated customer loyalty programs
When retailers try to track and reward their most loyal customers, it often results in additional repetitive tasks involved, depending on campaign complexity, that might cause a human employee to lose focus. Applying RPA to loyalty campaigns will increase the accuracy, speed, and reliability of the program, resulting in higher customer satisfaction.
One of the simplest examples of RPA use would be automatic selection and grouping customers based on what they’re buying, and sending targeted marketing messages to those who reach a certain order value or a number of purchases. For example, each customer that spends over $300 can automatically receive a discount code by email or through SMS.
Depending on the complexity of loyalty programs and campaigns RPA can do much more. For example, if a company requires customers to send in proof of purchases, like receipts or invoices, they can be automatically collected, read (with the use of ABBYY Optical Character Recognition /OCR in UiPath), and verified to avoid fraudulent entries. Verified data would then be added to the customer database and invalid entries proceeded to review by human employees.
EOD and Month-end Reporting with RPA
Proper reporting in retail is essential to keep track of what is going on in the business and make well-informed decisions, related to stock orders, staff schedules, promotions, and many others. The main problem with reporting concerns the manual part, as humans make mistakes – and making decisions based on wrong information has severe consequences.
One of the main benefits of RPA software use is that, when properly implemented, they can give 100% accuracy in reporting. A good use case of robots for reporting in retail was described by UiPath and concerned a “world-leading retail and wholesale business, with a presence in over 25 countries and more than 2 million employees globally”.
The company identified processes that had the highest potential for automation in reporting, and one of them concerned the “Back office retail file report” in its Brazilian stores. All the reports from hundreds of stores closing on the day before were used so that store managers could validate the closing information for each cash register. Those reports were time-consuming and error-prone and RPA was a perfect fit to solve the problem.
After automating, the streamlined “Back office retail file report” process looks like that:
- report for each store is kept in its dedicated individual FTP server,
- UiPath Robot reads the input from the terminal and gathers all the information,
- robot accesses each FTP server and downloads the file,
- in the end, it aggregates all the reports and saves them into a shared drive.
As reported, implementing RPA has brought immediate results with achieving 100% process accuracy.
Integrating brick-and-mortar stores and e-commerce platforms with RPA
Most major retailers already have or will have soon e-commerce platforms, but integrating data gathered from physical locations and online sources can be challenging. RPA software makes this process easy and fast, as it can access each system and collect data from it, export them in the desired format and repeat this process as frequently as needed, without fatigue and mistakes.
Retailers can benefit from this in cases such as:
- unification of customer experience – RPA software can not only help in data collection, to understand customers needs but also help to use them for example for cross-platform marketing campaigns,
- showing real-time availability of items in stores, to give customers that need them quickly information where they can purchase without waiting,
- combining data from online and offline sales for loyalty programs – this can be harder when different POS is used, and RPA combines such data easily.
Human resources and accounting in retail with RPA
Because of its flexibility and ease of implementation, Robotic Process Automation software can be applied to multiple processes carried out by a retail company, from very simple tasks to more complex activities.
Most frequently described use cases of RPA include:
Administration, tax, and finance department:
- accounts payable,
- payment processing,
- bank reconciliation,
- tax reporting.
Multiple retailers use for example RPA for Invoice Processing, which is not only a time-consuming task but is also very repetitive. When bots are implemented, collecting data, segregating them and processing bills becomes much faster and the number of errors is drastically reduced.
Human resources department:
- travel and expense management,
- employees master data management,
- time record validation.
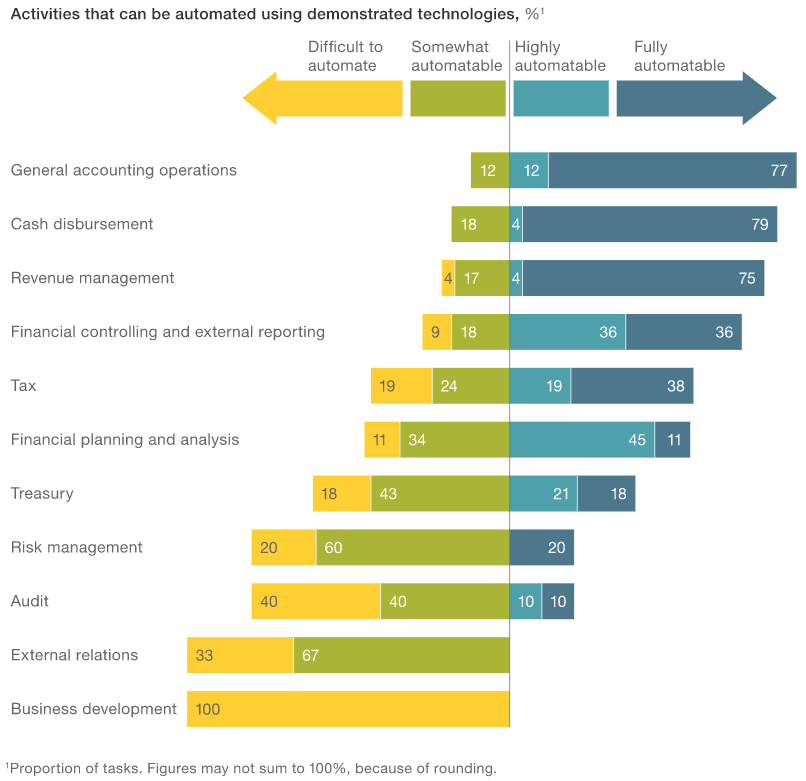
Financial and accounting operations are especially good candidates for automation, as they are largely rule-based, very manual, and virtually always carried out within IT systems. This is confirmed in the McKinsey report, pointing out various business areas and their potential for business process automation: